determining mean electrical axis couting boxes Based on the triangle, we constitute the hexagonal radial axis. This axis is what we use as. If there is a certain lead, that has a QRS of 0 (or close to that value), look at the perpendicular . Whether you're creating intricate designs in wood, precise cuts in metal, or detailed engravings on glass and plastic, CNC routers offer unmatched versatility and accuracy. In the past, achieving such precision manually was arduous and often led to inconsistent results.
0 · normal electrical axis explained
1 · net electrical axis
2 · mean electrical axis lab questions
3 · mean electrical axis formula
4 · mean electrical axis explained
5 · mean electrical axis diagnosis
6 · how to determine electrical axis
7 · how to calculate mean electrical axis
$595.00
We have provided a concise overview of the knowledge required to interpret the mean electrical axis on the 12-lead ECG. In essence, the QRS electrical axis is useful because it helps determine the position of the heart in .

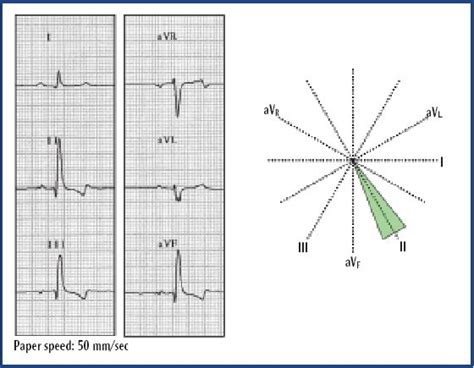
There are a few methods of measuring the MEA; two are described here. Using this method provides a quick system and, with practice, the MEA can often be ‘eyeballed’ to see whether it .The mean QRS axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. In most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ECG interpretation.Based on the triangle, we constitute the hexagonal radial axis. This axis is what we use as. If there is a certain lead, that has a QRS of 0 (or close to that value), look at the perpendicular .Step 3c: Calculate the electrical axis Approximate the net QRS deflection for leads I and aVF. Remember that the mean QRS axis will be oriented towards the lead with the greatest positive .
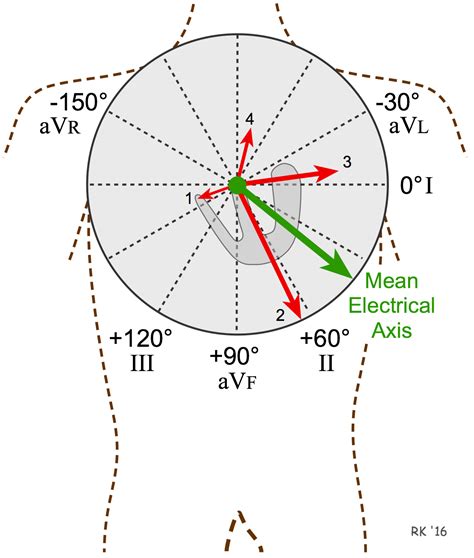
The mean QRS axis is oriented towards the lead with the greatest net QRS deflection. To calculate the net QRS deflection, add up the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the R wave (positive deflection), and . The average direction and magnitude of the depolarisation wave through the ventricles are together termed the mean electrical axis (MEA) or the cardiac axis. The MEA is .
Rate Calculating the mean electrical axis is a simple and rapid diagnostic procedure that should be considered part of routine ECG analysis. Shifts in the mean electrical axis, in conjunction with radiographic changes, can help you diagnose cardiac chamber enlargement and conduction defects.
We have provided a concise overview of the knowledge required to interpret the mean electrical axis on the 12-lead ECG. In essence, the QRS electrical axis is useful because it helps determine the position of the heart in the chest, patency of electrical pathways, and integrity of muscle mass.
There are a few methods of measuring the MEA; two are described here. Using this method provides a quick system and, with practice, the MEA can often be ‘eyeballed’ to see whether it is normal or abnormal.What do you need in order to determine the mean electrical axis? Interpret the ECG Pt 1 - Gelzer Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.The mean QRS axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. In most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ECG interpretation.
Based on the triangle, we constitute the hexagonal radial axis. This axis is what we use as. If there is a certain lead, that has a QRS of 0 (or close to that value), look at the perpendicular lead. The mean electrical axis will be in the direction of that lead. They are unipolar leads.Step 3c: Calculate the electrical axis Approximate the net QRS deflection for leads I and aVF. Remember that the mean QRS axis will be oriented towards the lead with the greatest positive net QRS deflection.The mean QRS axis is oriented towards the lead with the greatest net QRS deflection. To calculate the net QRS deflection, add up the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the R wave (positive deflection), and subtract the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the Q and S waves (negative deflection). The average direction and magnitude of the depolarisation wave through the ventricles are together termed the mean electrical axis (MEA) or the cardiac axis. The MEA is used mainly to assist in the assessment of ventricular enlargement and in the recognition of intraventricular conduction defects.
Rate Calculating the mean electrical axis is a simple and rapid diagnostic procedure that should be considered part of routine ECG analysis. Shifts in the mean electrical axis, in conjunction with radiographic changes, can help you diagnose cardiac chamber enlargement and conduction defects. We have provided a concise overview of the knowledge required to interpret the mean electrical axis on the 12-lead ECG. In essence, the QRS electrical axis is useful because it helps determine the position of the heart in the chest, patency of electrical pathways, and integrity of muscle mass.There are a few methods of measuring the MEA; two are described here. Using this method provides a quick system and, with practice, the MEA can often be ‘eyeballed’ to see whether it is normal or abnormal.
What do you need in order to determine the mean electrical axis? Interpret the ECG Pt 1 - Gelzer Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.The mean QRS axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. In most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ECG interpretation.
Based on the triangle, we constitute the hexagonal radial axis. This axis is what we use as. If there is a certain lead, that has a QRS of 0 (or close to that value), look at the perpendicular lead. The mean electrical axis will be in the direction of that lead. They are unipolar leads.Step 3c: Calculate the electrical axis Approximate the net QRS deflection for leads I and aVF. Remember that the mean QRS axis will be oriented towards the lead with the greatest positive net QRS deflection.The mean QRS axis is oriented towards the lead with the greatest net QRS deflection. To calculate the net QRS deflection, add up the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the R wave (positive deflection), and subtract the number of small squares that correspond to the height of the Q and S waves (negative deflection). The average direction and magnitude of the depolarisation wave through the ventricles are together termed the mean electrical axis (MEA) or the cardiac axis. The MEA is used mainly to assist in the assessment of ventricular enlargement and in the recognition of intraventricular conduction defects.

normal electrical axis explained
cnc stainless steel grinding parts suppliers
$26.99
determining mean electrical axis couting boxes|net electrical axis